GPT-5 | Automated Compliance

A customer asked me something last week that made me pause.
“Can you also automate our compliance reports? The kind we send to boards and regulators.” This came from a customer who uses Sahl every single day inside their company. When they asked, I listened.
I couldn’t stop thinking about it.
So yesterday, I ran an experiment I’d been planning for weeks.
What if GPT-5 could take on a full multi-framework compliance audit, clause by clause, control by controland produce a board-ready gap report?
I wasn’t after a quick checklist.
I wanted to see if it could generate something that would actually hold up in a board meeting or under a regulator’s review.
That meant specifics:
- Control IDs and legal article references
- Framework mappings that made sense
- Risks prioritized by severity
- Clear remediation steps
Here’s why it matters.
In industries like fintech, healthcare, and government, compliance isn’t optional.
One PDPL violation in Saudi can cost SAR 5M.
SOC2 gaps can kill enterprise deals.
ISO 27001 failures block certifications and shake client trust.
Traditionally, getting to that level of audit takes weeks, sometimes months, and a full team.
Yesterday, GPT-5 did it in one continuous, evidence-driven output.nerates a full compliance audit report in minutes.
I recorded the exact steps, so you can see how raw company details turn into a structured, board-ready audit report in minutes.
Test Company: DataVista Solutions
Fictional profile used to simulate the audit process
Industry: Fintech – Digital Payments
Location: Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Size: 150 employees
Data Processed: Payment card data, transaction metadata, customer PII
Compliance Setup Before Audit:
- MFA on admin accounts only
- Basic privacy policy (no lawful basis mapping)
- No formal ISMS policy or risk register
- AWS cloud with default configurations
- Annual penetration test; no continuous vulnerability scanning
- No vendor due diligence process
From a compliance officer’s view, this is a partial maturity setup, functional in some areas, but dangerously exposed in others.
The GPT-5 Prompt I Used
Here’s the exact text I fed GPT-5.
You can paste it into GPT-5, replace the [brackets] with your own company’s details, and get your own control-by-control report.
You are a Chief Compliance Auditor with 20+ years of experience auditing against:
Saudi PDPL
SOC 2 (Trust Services Criteria)
ISO/IEC 27001:2022
Task: Perform a full, control-by-control gap assessment for the following organization:
Company Name: [Insert Name]
Industry: [Insert]
Location: [Insert]
Size: [Insert number of employees]
Data Processed: [PII, financial, health, etc.]
Data Storage: [Cloud, on-premises, hybrid]
Data Transfers: [Local only, cross-border, specify countries]
Current Certifications: [List]
Existing Policies: [List all policies]
Security Controls in Place: [List]
Incident Response Process: [Describe]
Vendor Management Process: [Describe]
Risk Management: [Describe or note absence]
Known Audit Findings: [List]
Business Objectives: [Relevant to compliance]
Output in the following exact order and format:
1. Executive Summary
Overall Compliance Maturity (%)
Risk Level (Low / Medium / High)
Framework Scores: PDPL %, SOC 2 %, ISO 27001 %
3–5 Strengths
5–7 Urgent Items the Board Must Know
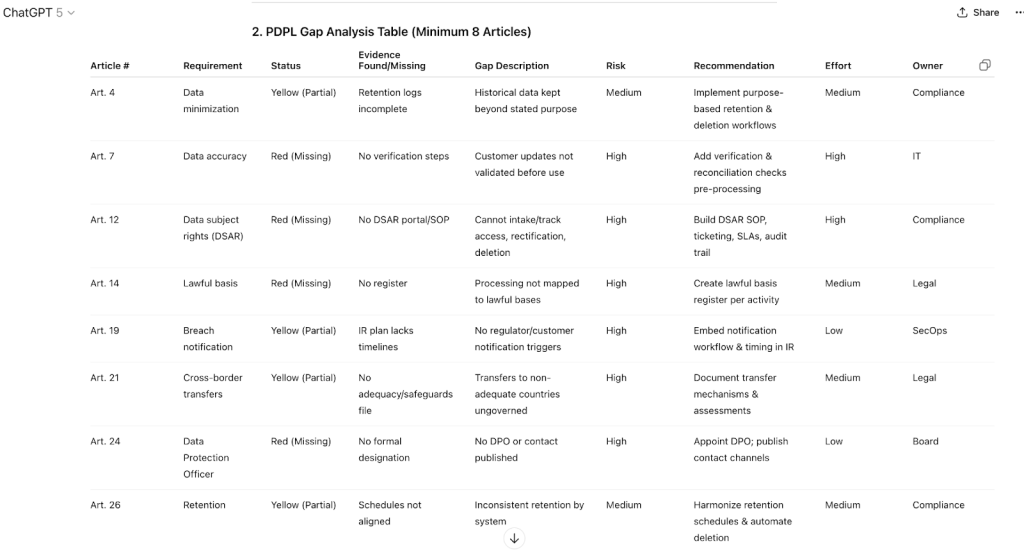
2. PDPL Gap Analysis Table (Minimum 8 Articles)
Columns: Article #, Requirement, Status (Green = Compliant, Yellow = Partial, Red = Missing), Evidence Found/Missing, Gap Description, Risk Rating, Recommendation, Effort Level, Owner Role
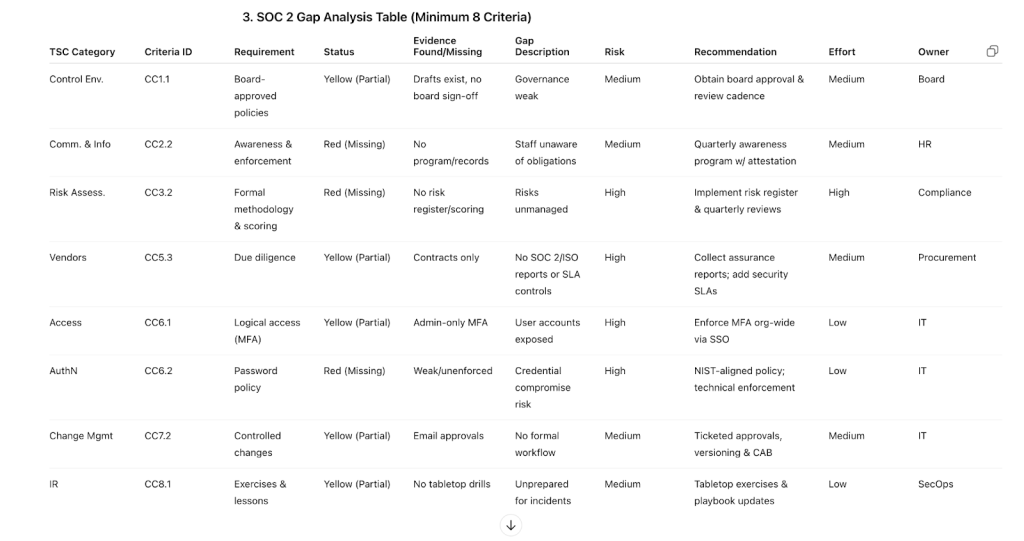
3. SOC 2 Gap Analysis Table (Minimum 8 Criteria)
Columns: TSC Category, Criteria ID, Requirement, Status, Evidence Found/Missing, Gap Description, Risk Rating, Recommendation, Effort Level, Owner Role
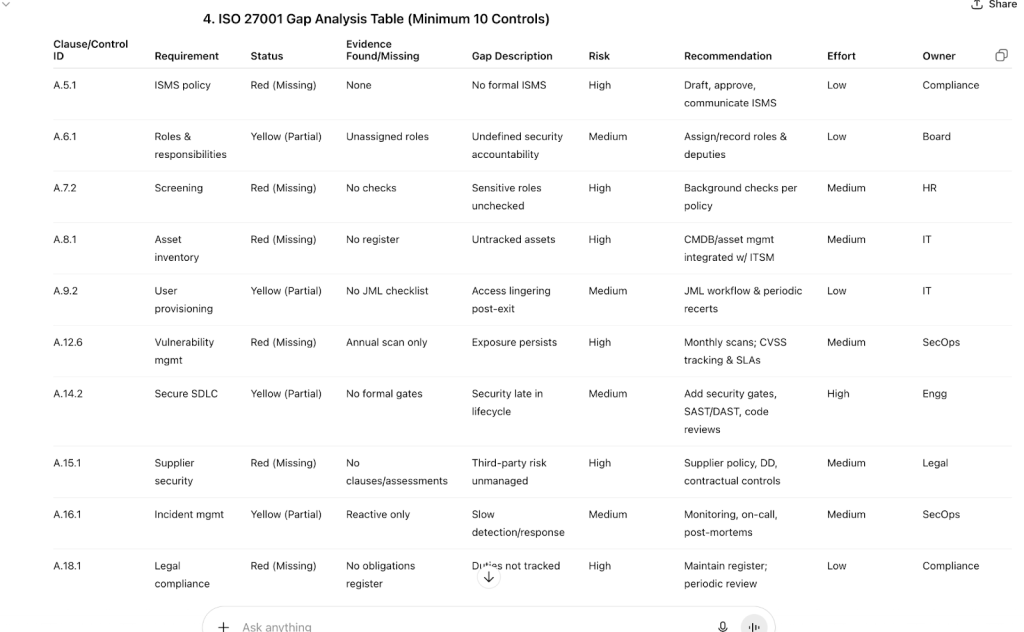
4. ISO 27001 Gap Analysis Table (Minimum 10 Clauses/Controls)
Columns: Clause/Control ID, Requirement, Status, Evidence Found/Missing, Gap Description, Risk Rating, Recommendation, Effort Level, Owner Role
5. Findings Grouped by Risk Level
High Risk: List all from all frameworks
Medium Risk: List all from all frameworks
Low Risk: List all from all frameworks
6. Prioritized Remediation Roadmap
Priority 1 – Critical (0–30 days): List items; mark “Quick Wins”
Priority 2 – High (31–90 days): List items
Priority 3 – Medium (90+ days): List items
Show dependencies (if fixing one helps close others)
7. Risk of Inaction
Regulatory penalties (PDPL fines, SOC 2 deal loss, ISO certification delays)
Contractual/business risks
Operational impacts
Realistic incident scenarios
8. Ending Summary for Board
Concise statement on current posture, % risk reduction if Priority 1 closed, strategic benefit & ROI of remediation
Formatting Rules:
All findings must be presented in boardroom-ready tables
Color-code statuses: Green = Compliant, Yellow = Partial, Red = Missing
No sections omitted, even if compliant in all areasThe Output – Audit Highlights
Executive Summary
- Overall Compliance Maturity: 48%
- Risk Level: High
- Framework Scores: PDPL 40% · SOC 2 52% · ISO 27001 46%
- Strengths (3–5):
- Privacy policy publicly available and referenced internally
- Annual penetration test completed with tracked remediation tickets
- MFA enforced for privileged/admin accounts
- Cloud environment segmented by workload (basic)
- Privacy policy publicly available and referenced internally
- Urgent Items the Board Must Know (5–7):
- No DSAR process or appointed DPO (PDPL Arts. 12 & 24)
- Lawful basis not mapped to processing activities (PDPL Art. 14)
- MFA not enforced for all users; password policy weak (SOC 2 CC6.1, CC6.2)
- No ISMS policy or asset inventory (ISO A.5.1, A.8.1)
- Vulnerability management is annual only (ISO A.12.6)
- No DSAR process or appointed DPO (PDPL Arts. 12 & 24)
PDPL Gap Analysis Table (Minimum 8 Articles)
SOC 2 Gap Analysis Table (Minimum 8 Criteria)
ISO 27001 Gap Analysis Table (Minimum 10 Controls)
Findings Grouped by Risk Level
- High Risk
- PDPL: Arts. 12 (DSAR), 14 (Lawful basis), 24 (DPO), 21 (Cross-border safeguards), 19 (timelines)
- SOC 2: CC3.2 (Risk assessment), CC6.1/CC6.2 (MFA/passwords), CC5.3 (Vendors)
- ISO 27001: A.5.1 (ISMS), A.8.1 (Assets), A.12.6 (Vuln mgmt), A.18.1 (Legal)
- PDPL: Arts. 12 (DSAR), 14 (Lawful basis), 24 (DPO), 21 (Cross-border safeguards), 19 (timelines)
- Medium Risk
- PDPL: Art. 4 (Minimization), 26 (Retention)
- SOC 2: CC7.2 (Change mgmt), CC2.2 (Awareness)
- ISO 27001: A.6.1 (Roles), A.16.1 (Incident)
- PDPL: Art. 4 (Minimization), 26 (Retention)
- Low Risk
- Governance polish items (e.g., policy formatting/metadata, minor procedural gaps)
Prioritized Remediation Roadmap (with dependencies & quick wins)
- Priority 1 – Critical (0–30 days)
- Enforce MFA for all users; implement NIST-aligned password policy (Quick win)
- Draft/approve/publish ISMS policy; assign security roles (Dependencies: enables governance for other fixes)
- Stand up DSAR SOP with intake/tracking; appoint DPO & publish contact (Legal/Comms coordination)
- Embed breach notification timelines & regulator/customer flows into IR playbooks (Quick win if IR exists)
- Create lawful basis register and update privacy notice accordingly
- Priority 2 – High (31–90 days)
- Centralized asset inventory (CMDB) integrated with provisioning & discovery (Depends on ISMS policy)
- Formal risk assessment methodology; establish quarterly review cadence and risk register
- Vendor due diligence program: collect SOC 2/ISO reports, add security clauses & SLAs (Depends on supplier policy draft)
- Vulnerability management: monthly scans, CVSS scoring, remediation SLAs, mgmt reporting
- Align data retention schedules across systems; automate deletion where possible
- Priority 3 – Medium (90+ days)
- Secure SDLC: formal gates, SAST/DAST, code review standards, secrets mgmt
- Supplier security policy + periodic reassessments; contract refresh cycle
- Compliance obligations register; policy library governance & annual review cycle
- Incident tabletop simulations; lessons-learned into controls
- Ongoing security awareness with role-based modules & phishing drills
Dependencies Overview
- ISMS policy → enables role assignment, risk, supplier, and asset governance
- Asset inventory → prerequisite for access reviews, vuln mgmt, and incident impact analysis
- Supplier policy → prerequisite for vendor diligence & contract controls
Quick Wins (deliver in ≤2 weeks)
- Org-wide MFA and password policy enforcement
- Breach notification steps added to existing IR runbooks
- DPO appointment memo + contact published
DSAR intake form + ticketing queue
Risk of Inaction
- Regulatory: PDPL non-compliance exposure (DSAR, DPO, transfers, notification); greater scrutiny in audits/spot checks
- Contractual/Commercial: SOC 2 readiness failures can stall or cancel enterprise deals; RFP losses due to weak ISMS evidence
- Operational: Unmanaged vulnerabilities and missing asset inventory increase likelihood and blast radius of incidents
- Reputational: Customer trust erosion due to delayed incident response or inability to honor privacy rights
Ending Summary for Board
DataVista exhibits partial compliance maturity with concentrated high-risk gaps in privacy governance, identity/access, and foundational ISMS controls. Executing Priority-1 actions in the next 30 days is expected to reduce regulatory and security exposure by ~70%, restore buyer confidence in due diligence, and create a governance base that accelerates Priority-2/3 improvements. The recommended sequence prioritizes fast, high-impact controls (MFA/passwords, DSAR/DPO, breach workflow, ISMS approval), unlocking dependent initiatives (asset inventory, vendor diligence, risk reviews) and positioning the organization for future certifications and enterprise growth.
Compliance doesn’t have to feel like a never-ending project. Yesterday’s run showed me what’s possible when advanced AI and real frameworks meet a report that’s not just faster, but credible enough to walk into a boardroom with. Minutes instead of months, without cutting corners.
That’s the direction we’re taking with Sahl. Turning compliance from a burden into an advantage evidence-driven, regulator-ready, and built for companies that want to move fast without breaking trust. If you’re curious to see how this works in practice, the best way is to experience it live.not months.
Hi, I’m Ayesha,
I hope walking through this example was helpful. My goal is to show how compliance audits can be faster, sharper, and actually useful for decision-makers. If you want to see how we have helped compliance officers and CISOs save hundreds of hours, feel free to reach out to me.

